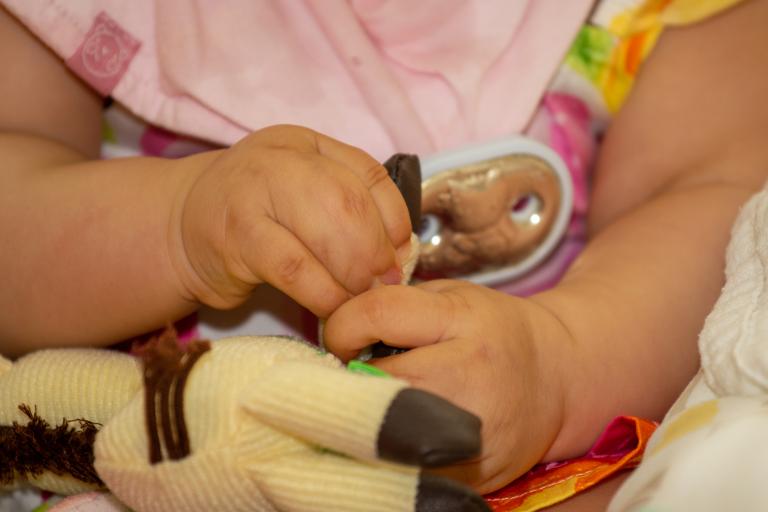
Syndactyly Release (Webbed or Joined Fingers or Toes)
What is Syndactyly?
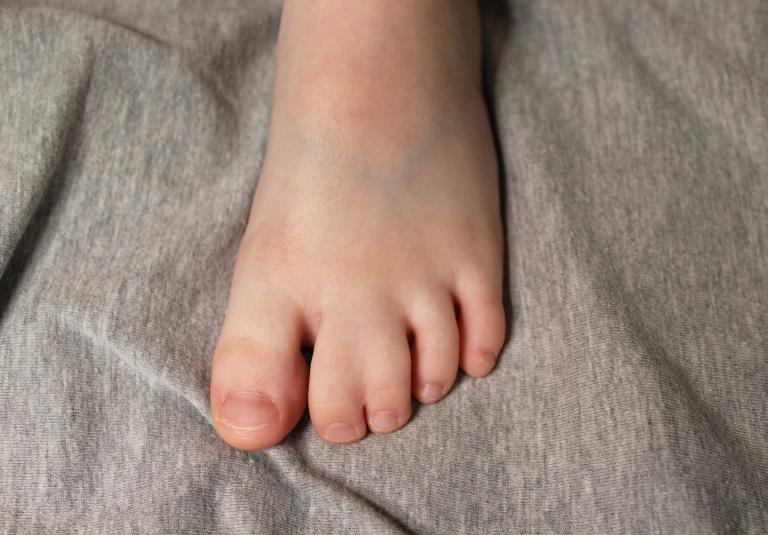
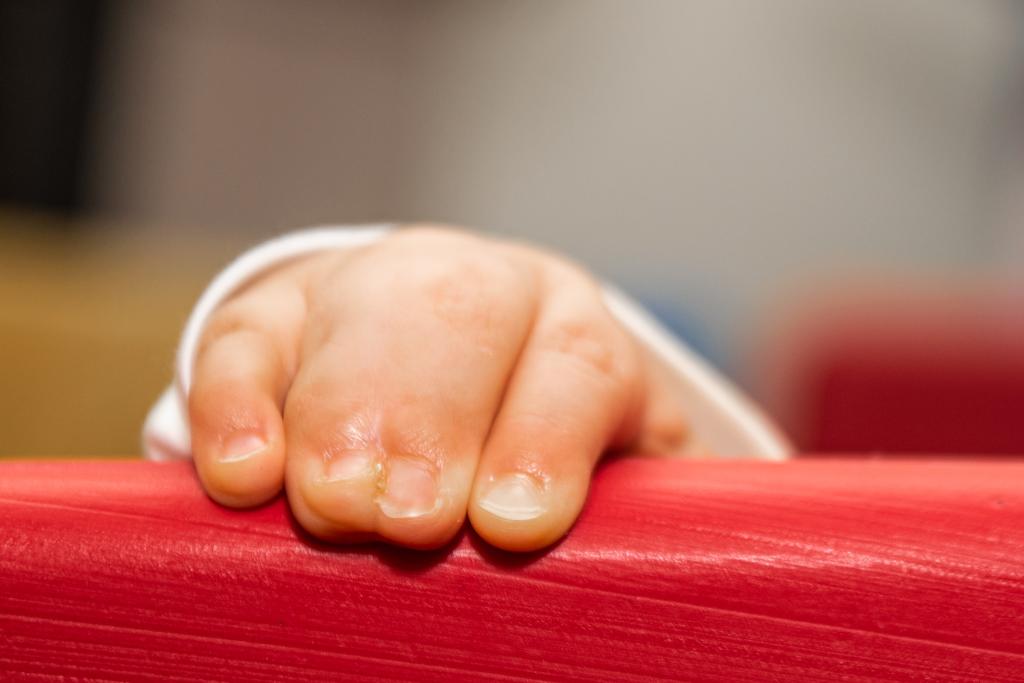
Syndactyly is the medical term for webbed or conjoined fingers or toes. Syndactyly is the most common malformation of the limbs, affecting about one in every 2,000-3,000 children born each year.
It can be an isolated condition or may be associated with other birth differences or conditions for your child. When only your child’s fingers or toes is affected, syndactyly release can provide for independent finger movement and function, depending on the nature and severity of the condition. In simple syndactyly the join of the fingers is just soft tissue (skin) and corrective surgery is aimed to carefully separate the digits while preserving the nerve supply/sensation to the finger tips.
 Treatment
Treatment